In the realm of decision-making and risk assessment, businesses often employ various analytical techniques to evaluate potential outcomes and uncertainties. Among these techniques, scenario analysis and sensitivity analysis stand out as indispensable tools. While both aim to enhance decision-making by assessing different factors, they approach uncertainty in distinct ways. In this article, we delve into the concepts, examples, applicability, advantages, and limitations of scenario analysis vs sensitivity analysis.
Scenario Analysis Vs Sensitivity Analysis
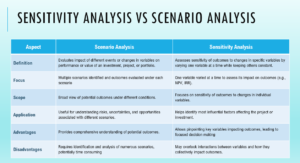
Scenario analysis and sensitivity analysis are both techniques used in financial modeling and risk management to evaluate the potential outcomes of different situations. Scenario analysis involves assessing the impact of various hypothetical events or changes in variables on the performance or value of an investment, project, or portfolio. It typically identifies multiple scenarios and evaluates the outcomes under each scenario. In contrast, sensitivity analysis focuses on assessing the sensitivity of a project or investment to changes in specific variables by varying one variable at a time while keeping others constant.
While scenario analysis provides a broader view of potential outcomes under different conditions, sensitivity analysis delves into the sensitivity of outcomes to changes in individual variables, helping to identify the most influential factors. Both techniques are valuable tools in decision-making, enabling stakeholders to understand risks, uncertainties, and opportunities associated with different scenarios and variables, and develop strategies to mitigate risks and maximize returns.
What is Scenario Analysis?
Scenario analysis is a method used to assess the potential impact of various future events or conditions on a particular decision, strategy, or project. It involves constructing a set of scenarios representing different plausible future states, and then evaluating the outcomes under each scenario. Each scenario typically represents a different combination of key variables or assumptions, allowing decision-makers to understand the range of possible outcomes and associated risks.
Scenario analysis typically involves three main steps;
- Identifying relevant scenarios: This step involves identifying and defining the different scenarios or potential events that could affect the investment or project. These scenarios could include changes in economic conditions, market trends, regulatory changes, or other factors specific to the investment.
- Developing assumptions: For each scenario, assumptions are made regarding how the relevant variables would change and how they would impact the investment or project. These assumptions are often based on historical data, expert judgment, market research, or other sources of information.
- Analyzing outcomes: Once the assumptions for each scenario are defined, the impact on key performance indicators or financial metrics is analyzed. This could include measures such as revenue, expenses, cash flow, profitability, or the value of the investment or project.
Scenario analysis helps decision-makers understand the potential risks and opportunities associated with different scenarios and make more informed decisions. It allows them to assess the sensitivity of their investments or projects to changes in key variables and develop strategies to mitigate risks or capitalize on opportunities.
Example: Consider a retail company planning to expand its operations into a new market. It might develop scenarios based on different economic conditions, consumer behaviors, and competitive landscapes. These scenarios could include optimistic, moderate, and pessimistic projections of sales, costs, and market share, helping the company assess the viability of its expansion strategy under various circumstances.
In another example, a company is considering investing in a new product line. The company performs scenario analysis to assess the potential impact of different market conditions on the profitability of the investment.
Scenarios identified:
- Base Case: Moderate economic growth and stable market conditions.
- Optimistic Scenario: Strong economic growth and high demand for the new product.
- Pessimistic Scenario: Economic downturn and weak demand for the new product.
Assumptions for each scenario:
- Base Case: 5% annual growth in sales, 20% profit margin.
- Optimistic Scenario: 10% annual growth in sales, 25% profit margin.
- Pessimistic Scenario: 2% annual growth in sales, 15% profit margin.
Outcome analysis:
- Base Case: Net present value (NPV) of $1 million.
- Optimistic Scenario: NPV of $2 million.
- Pessimistic Scenario: NPV of $500,000.
Based on the scenario analysis, the company may decide to proceed with the investment in the new product line, as the base case and optimistic scenarios yield positive NPVs. However, the company may also develop contingency plans to address potential challenges in the pessimistic scenario, such as cost-cutting measures or alternative marketing strategies.
Overall, scenario analysis helps decision-makers assess the potential risks and rewards associated with different scenarios and make more informed decisions to achieve their objectives.
Advantages of Scenario Analysis
- Holistic Perspective: Considers multiple potential futures, providing a comprehensive view of risks and opportunities.
- Scenario Planning: Facilitates strategic planning by fostering discussions and generating insights into alternative courses of action.
- Risk Mitigation: Enables proactive risk management by identifying potential threats and developing contingency plans.
Limitations of Scenario Analysis
- Subjectivity: Scenarios are based on assumptions and interpretations, making them inherently subjective and prone to bias.
- Complexity: Developing and analyzing multiple scenarios can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for complex systems or environments.
- Limited Predictive Power: While scenario analysis helps explore possibilities, it does not predict the likelihood of specific outcomes or the timing of events.
What is Sensitivity Analysis?
Sensitivity analysis, on the other hand, focuses on understanding how changes in specific input variables or assumptions affect the outcomes of a decision model or project. It identifies the variables that have the most significant impact on the results and quantifies the extent of this impact. By systematically varying the input variables within a predefined range, sensitivity analysis enables decision-makers to gauge the robustness of their decisions to changes in key factors.
Example : Suppose a manufacturing company is evaluating the financial feasibility of a new product. Through sensitivity analysis, it may examine how variations in factors such as production costs, selling price, and demand volume affect the project’s net present value (NPV). By determining which variables exert the most influence on NPV, the company can focus its attention on managing or mitigating the associated risks.
Advantages of Sensitivity Analysis
- Focus on Key Variables: Identifies the most influential factors driving decision outcomes, enabling targeted risk management efforts.
- Quantitative Insights: Provides quantitative measures of sensitivity, allowing decision-makers to prioritize resources and interventions effectively.
- Flexibility: Can be applied to various decision models and scenarios, offering valuable insights across different contexts and domains.
Limitations of Sensitivity Analysis
- Assumption Dependency: Results are contingent on the accuracy and validity of input assumptions, which may introduce uncertainties.
- Interactions Complexity: Ignores potential interactions and dependencies among variables, potentially leading to oversimplified conclusions.
- Limited Scope: Focuses on isolated changes in individual variables, overlooking broader systemic effects and nonlinear relationships.
In conclusion, both scenario analysis and sensitivity analysis are invaluable tools for decision-makers grappling with uncertainty and complexity. While scenario analysis provides a holistic view of potential futures, sensitivity analysis offers insights into the relative importance of key variables. By leveraging these techniques in tandem, organizations can enhance their strategic foresight, mitigate risks, and make more informed decisions in an ever-changing business landscape.
