In today’s dynamic and uncertain business environment, organizations face a multitude of risks that can impact their operations, objectives, and reputation. From economic volatility and regulatory changes to cybersecurity threats and supply chain disruptions, businesses must navigate a complex landscape of uncertainties to achieve sustainable success. This is where a robust risk management framework comes into play, providing a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks effectively.
What is a Risk Management Framework?
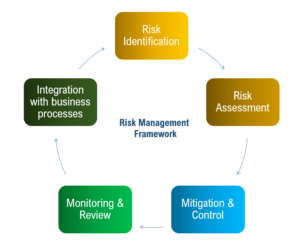
A risk management framework is a structured process that guides organizations in managing risks systematically across all levels and functions. It serves as a foundation for establishing risk management policies, procedures, and practices tailored to the organization’s unique needs and objectives. The framework outlines the steps and components necessary to identify, assess, prioritize, and respond to risks in a consistent and coordinated manner.
Key Components of a Risk Management Framework
Risk Identification
The first step in the risk management process involves identifying potential risks that could affect the organization’s objectives. This may include internal and external risks across various categories, such as strategic, financial, operational, compliance, and reputational risks. Techniques such as risk assessments, brainstorming sessions, and historical data analysis can help uncover both known and emerging risks.
Risk Assessment
Once risks have been identified, they need to be assessed in terms of their likelihood and potential impact on the organization. Risk assessment involves analyzing the probability of occurrence and severity of consequences associated with each risk. Quantitative methods, such as probability analysis and financial modeling, as well as qualitative approaches like risk matrices and scenario analysis, are used to prioritize risks based on their significance.
Risk Mitigation and Control
After assessing risks, organizations develop and implement strategies to mitigate or control their impact. This may involve risk avoidance, risk reduction through preventive measures, risk transfer (e.g., insurance), risk sharing through partnerships or contracts, or acceptance of certain risks based on their tolerance levels. Risk mitigation measures are tailored to address specific risks and may involve a combination of technical, operational, and managerial controls.
Monitoring and Review
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and review to ensure its effectiveness. Organizations establish monitoring mechanisms to track changes in the risk landscape, assess the implementation of risk mitigation measures, and identify emerging risks or trends. Periodic reviews of the risk management framework enable organizations to adapt their strategies and practices to evolving business conditions and emerging threats.
Integration with Business Processes
A robust risk management framework is integrated into the organization’s overall governance, strategic planning, and decision-making processes. It ensures that risk considerations are embedded in key business activities, such as strategic planning, budgeting, project management, and performance evaluation. By integrating risk management into day-to-day operations, organizations can proactively identify and address risks, thereby enhancing their resilience and ability to achieve their objectives.
Benefits of a Risk Management Framework
Implementing a comprehensive risk management framework offers several benefits to organizations, including:
-
- Enhanced Decision-Making: A structured risk management framework provides decision-makers with valuable insights into potential risks and opportunities. By systematically identifying and assessing risks, organizations can make informed decisions and allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that strategic objectives are pursued with greater confidence and clarity.
- Improved Resilience: Proactive risk management enhances an organization’s resilience in the face of uncertainty and adversity. By identifying and mitigating potential threats, organizations can better withstand disruptions such as economic downturns, natural disasters, supply chain interruptions, and cybersecurity breaches. This resilience enables businesses to maintain continuity of operations, minimize downtime, and recover more quickly from adverse events.
- Protection of Assets and Reputation: Effective risk management safeguards the organization’s assets, investments, and reputation from potential harm. By identifying and addressing risks that could impact financial stability, brand image, or customer trust, organizations can mitigate the potential for financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. This protection is vital for preserving shareholder value and maintaining stakeholder confidence.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: A robust risk management framework helps organizations stay compliant with regulatory requirements and industry standards. By systematically assessing and managing risks related to legal, regulatory, and ethical obligations, organizations can reduce the risk of non-compliance, avoid fines and penalties, and maintain the trust and confidence of regulators, customers, and other stakeholders.
- Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains: Effective risk management can lead to cost savings and efficiency gains across the organization. By identifying and mitigating risks that could lead to operational disruptions, financial losses, or resource wastage, organizations can minimize unnecessary expenditures, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall operational efficiency. This results in greater profitability and competitive advantage in the marketplace.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Confidence: Demonstrating a commitment to sound risk management practices enhances stakeholder confidence and trust in the organization’s ability to manage uncertainties effectively. Investors, customers, employees, and other stakeholders are more likely to support and engage with organizations that prioritize risk management and demonstrate accountability for addressing potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Strategic Opportunities and Innovation: Effective risk management is not just about avoiding threats; it’s also about seizing opportunities for growth and innovation. By understanding and managing risks, organizations can identify strategic opportunities, explore new markets, and pursue innovative initiatives with confidence. This proactive approach to risk management fosters a culture of agility, creativity, and resilience, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage over the long term.
In summary, a well-implemented risk management framework offers numerous benefits to organizations, including enhanced decision-making, improved resilience, protection of assets and reputation, compliance with regulations, cost savings, stakeholder confidence, and strategic opportunities for growth and innovation. By prioritizing risk management as a strategic priority, organizations can navigate uncertainties effectively and achieve their objectives with greater confidence and success.