The McKinsey GE Matrix (also known as Mckinsey GE Nine box matrix), is a strategic planning tool designed to help businesses evaluate their portfolios of products, business units, or investments. It was developed by McKinsey & Company in collaboration with General Electric in the 1970s as a means to assist companies in making more informed decisions about where to allocate resources. This matrix is particularly valuable in complex organizations where multiple business units or product lines compete for limited resources.
Understanding the McKinsey GE Matrix
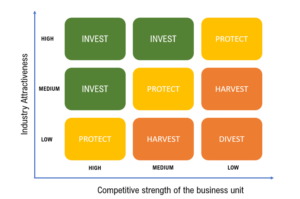
The McKinsey GE Matrix is a 3×3 grid that evaluates business units or products based on two key dimensions: Industry Attractiveness and Business Unit Strength.
Industry Attractiveness of Each Strategic business unit
This dimension assesses the overall appeal of the industry or market in which the business opertes. It takes into account the following factors;
- Market size,
- Market growth rate,
- Profitability,
- Competitive intensity,
- Technological advancements;
- Customer segmentation
- Regulatory environment
Industries that score high on these factors are considered more attractive.
Business Unit Strength of each Strategic Business unit
This dimension evaluates the competitive strength and capabilities of a particular business unit or product within its industry. The factors which are looked at are;
- Market share,
- Brand reputation,
- Product quality,
- Product differentiation;
- Production capacity;
- Pricing power;
- Operational efficiency
- Customer loyalty
Business units that have a strong competitive position are scored higher.
The Nine-Box Matrix
The matrix is divided into nine cells, representing different strategic scenarios. These cells are categorized into three broad zones:
- Grow (Invest/Expand): Units in the top right of the matrix (high industry attractiveness and high business unit strength) are strong candidates for investment. These are seen as the “stars” of the portfolio with the potential for significant growth and return on investment .
- Protect(Selectively Invest/Manage for Earnings): Units in the middle cells (medium industry attractiveness or medium business unit strength) require a more balanced approach. They may still be profitable but might not justify significant new investments. The strategy here might be to maintain current levels of investment and manage these units carefully to sustain profitability .
- Divest (Harvest/Exit): Units in the bottom left of the matrix (low industry attractiveness and low business unit strength) are considered the weakest in the portfolio. These might be candidates for divestment, as they are unlikely to deliver strong returns in the future. Resources could be better utilized elsewhere .
Mckinsey GE Matrix – Relevance in Investment Prioritization
The McKinsey GE Matrix is particularly relevant for organizations with diverse portfolios, such as conglomerates or companies with multiple product lines. It helps in the following ways:
- Resource Allocation: By categorizing business units or products into different segments, the matrix guides management on where to allocate resources—whether to invest, hold, or divest. This ensures that resources are deployed in areas with the highest potential for growth and profitability.
- Strategic Focus: The matrix encourages companies to focus on areas where they have a competitive advantage and the market potential is high. It helps in identifying units that may require additional resources to exploit growth opportunities and those that might need restructuring or even closure.
- Risk Management: By considering both industry attractiveness and business unit strength, the matrix provides a balanced view of risk and return. Companies can avoid over-investing in attractive but weak business units or under-investing in strong units within less attractive industries.
Conclusion
The McKinsey GE Matrix remains a powerful tool for businesses looking to strategically manage their portfolios. By providing a clear framework for assessing industry attractiveness and business unit strength, it aids in making informed decisions about where to invest, hold, or divest.
