Effective management of accounts payables (AP) is crucial for maintaining liquidity, optimizing cash flow, and fostering strong vendor relationships. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as vital tools for measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of AP processes. In this article, we’ll explore the key KPIs that organizations should monitor to ensure successful accounts payables management and drive sustainable growth.
Key KPIs for Effective Accounts Payables Management
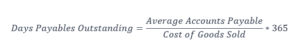
Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)
Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) is a fundamental KPI that measures the average number of days it takes for a company to pay its suppliers after receiving goods or services. A lower DPO indicates a shorter time frame for payment, while a higher DPO suggests delayed payments. Monitoring DPO helps businesses strike a balance between managing cash flow effectively and maintaining positive vendor relationships.
Invoice Processing Time
Invoice Processing Time measures the average time it takes for invoices to be processed from receipt to approval. A shorter processing time indicates greater efficiency in AP operations, leading to timely payments and improved vendor satisfaction. By streamlining invoice processing workflows and leveraging automation technologies, organizations can reduce processing time and enhance operational efficiency.
Invoice Accuracy Rate
Invoice Accuracy Rate measures the percentage of invoices processed without errors or discrepancies. High accuracy rates indicate effective validation processes and minimize the risk of payment errors or disputes. Implementing robust validation procedures, training staff on data entry best practices, and leveraging technology solutions can help improve invoice accuracy and enhance financial accuracy.
Percentage of Early Payment Discounts Captured
The Percentage of Early Payment Discounts Captured reflects the proportion of available discounts that the company is able to capture through early payment. Maximizing early payment discounts can result in significant cost savings and improve cash flow management. By implementing proactive payment strategies and leveraging vendor relationships, organizations can capture more discounts and optimize cash utilization.
Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
The Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio measures how quickly a company pays off its suppliers over a given period. A higher turnover ratio indicates efficient management of payables and effective cash flow management. Monitoring changes in turnover ratio over time can provide insights into payment trends and vendor relationships, helping organizations optimize their AP processes.
Percentage of Invoices Paid on Time
The Percentage of Invoices Paid on Time measures the proportion of invoices paid by the due date or within agreed-upon payment terms. High on-time payment percentages indicate effective cash flow management and positive vendor relationships. By prioritizing payments, monitoring payment deadlines, and implementing efficient payment processes, organizations can improve on-time payment performance.
Vendor Satisfaction Score
Vendor satisfaction score reflects the level of satisfaction among suppliers with the company’s accounts payable process. It can be measured through surveys, feedback forms, or vendor performance evaluations. Higher satisfaction scores indicate strong vendor relationships and efficient accounts payable management. Building strong vendor relationships is essential for successful AP management. Regularly assessing vendor satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, or performance evaluations can help identify areas for improvement and strengthen vendor partnerships.
Invoice Aging Analysis
Invoice aging analysis is a crucial Key Performance Indicator (KPI) in accounts payable management, providing valuable insights into the timeliness of invoice payments and the health of a company’s financial operations. By tracking the aging of outstanding invoices, organizations can identify payment trends, address delays, and optimize cash flow management.
Invoice aging analysis involves categorizing outstanding invoices based on their age or the length of time they remain unpaid. Typically, invoices are classified into predetermined time intervals, such as 30 days, 60 days, and 90 days past due. By organizing invoices in this manner, organizations can assess payment patterns, identify overdue invoices, and prioritize payment processing accordingly.
Also Read:
Percentage of Duplicate Payments
The percentage of duplicate payments KPI measures the proportion of payments made by a company that are duplicates—meaning the same invoice is paid more than once. Duplicate payments can occur due to various reasons, including human error, system glitches, and inadequate controls in the AP process. Tracking this KPI helps organizations identify instances of duplicate payments and take corrective actions to prevent future occurrences.
Monitoring the percentage of duplicate payments is essential for safeguarding financial resources, maintaining operational efficiency, and preserving vendor relationships. By implementing robust controls, leveraging technology solutions, enhancing data validation processes, and fostering effective vendor communication, organizations can minimize the risk of duplicate payments and strengthen their AP operations.
Cost per Invoice
The cost per invoice is calculated by dividing the total cost of AP operations by the number of invoices processed within a specific period. This metric includes various direct and indirect costs associated with invoice processing, such as labor, technology, overhead, and administrative expenses. Tracking the cost per invoice provides insights into the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of AP processes, helping organizations identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to streamline workflows and reduce expenses.
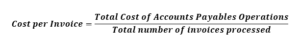
Cost of Accounts payables Operations includes Labour Cost (FTE cost), Technology Cost, Overhead and Administrative Costs.
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective management of accounts payables is essential for maintaining financial stability and driving business success. By monitoring key KPIs such as Days Payable Outstanding, Invoice Processing Time, Invoice Accuracy Rate, Percentage of Early Payment Discounts Captured, Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio, Percentage of Invoices Paid on Time, and Vendor Satisfaction Score, organizations can gain valuable insights into their AP processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement strategies to optimize AP management for enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and vendor relationships. By focusing on these key KPIs, organizations can unlock the full potential of their accounts payables function and achieve sustainable growth in the long run.

